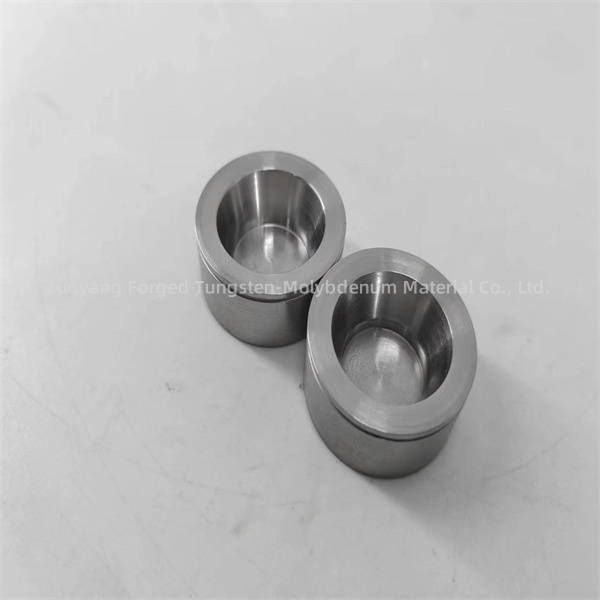
high temperature titanium crucible for furnace melting
The melting point of titanium is approximately 1,668 degrees Celsius (3,034 degrees Fahrenheit). This high melting point makes titanium suitable for high-temperature applications, including making crucibles for melting in furnaces and other processes that involve exposure to extreme heat.

At high temperatures, titanium undergoes a variety of changes and reactions. Some key behaviors of titanium at high temperatures include:
1. Oxidation: Titanium can react with oxygen at high temperatures to form a thin layer of titanium dioxide (TiO2) on its surface. This oxide layer provides the metal with excellent corrosion resistance, preventing it from further oxidation and degradation.
2. Strength retention: Titanium maintains its strength and integrity at high temperatures, allowing it to maintain structural stability in harsh environments. This property makes titanium a valuable material for aerospace, industrial processing and high-temperature engineering applications.
3. Phase change: At specific high temperatures, titanium can undergo phase change, changing its crystal structure and properties. These transformations can be used to tailor the properties of materials for specific applications.
4. Reactivity: Although titanium is generally resistant to corrosion, it can react with certain gases and elements at very high temperatures, resulting in the formation of titanium compounds and alloys.
Overall, titanium's behavior at high temperatures is characterized by its ability to maintain strength, resist oxidation, and undergo controlled phase changes, making it a versatile and reliable material for use in extreme high-temperature conditions.

Wechat:15138768150
WhatsApp: +86 15838517324
E-mail : jiajia@forgedmoly.com